This article explores the latest developments in cancer research and potential breakthroughs in treatment. With cancer being one of the leading causes of death worldwide, it is crucial to stay up-to-date with the latest developments in the field. This article provides a comprehensive overview of the latest research and potential breakthroughs, including new treatment approaches, novel therapies, and emerging technologies.
Cancer is a complex and challenging disease that affects millions of people worldwide. Despite significant progress in cancer research and treatment, it remains a leading cause of death globally.
According to the World Health Organization, cancer is responsible for an estimated 9.6 million deaths in 2018. However, recent advances in cancer research and treatment have provided new hope for patients and healthcare professionals alike.
Immunotherapy
Immunotherapy is an emerging field in cancer treatment that uses the body’s immune system to fight cancer cells. It has shown remarkable success in treating certain types of cancer, including melanoma, non-small cell lung cancer, and bladder cancer.
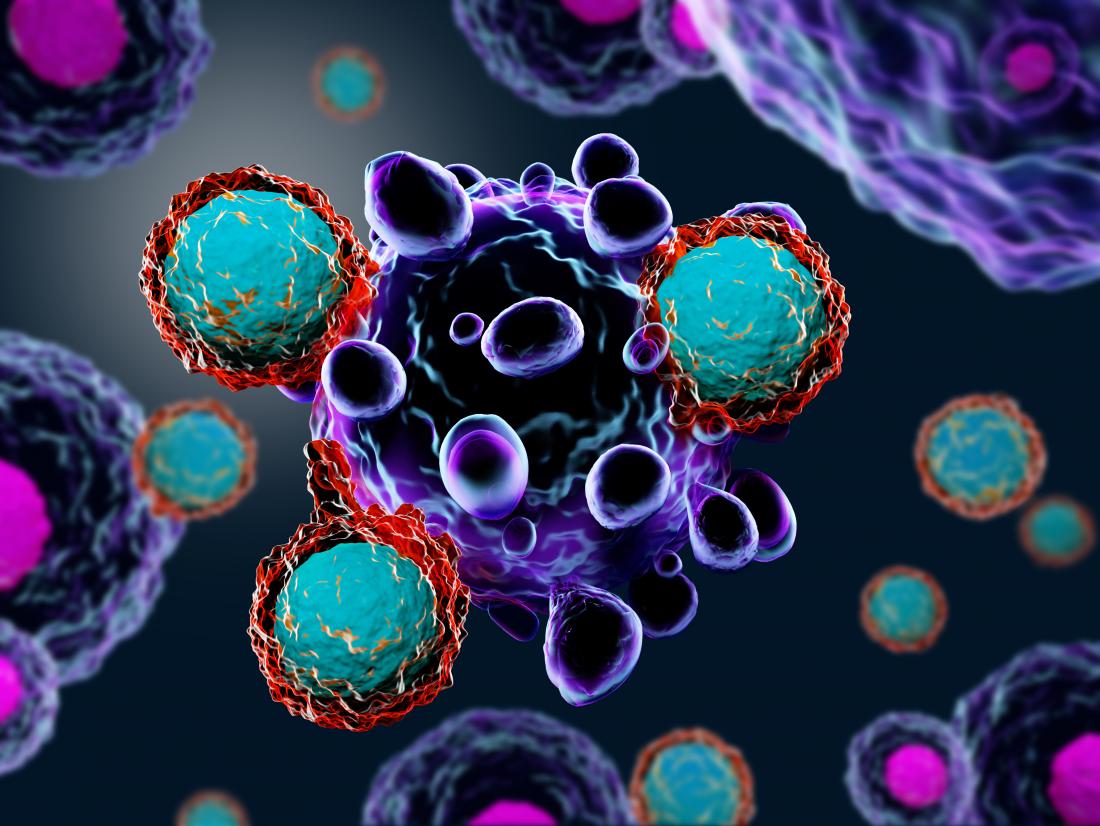
The approach involves using antibodies or other agents to stimulate the immune system to attack cancer cells. Researchers are continuing to explore new immunotherapies, including personalized vaccines that target specific mutations in cancer cells.
Genomics
Genomics is the study of genetic information, including DNA and RNA, and how it relates to health and disease. Recent advances in genomics have led to new approaches in cancer research and treatment.
Genomic sequencing has allowed researchers to identify specific genetic mutations in cancer cells, which can be targeted with precision medicine. This approach involves using drugs that target specific genetic mutations in cancer cells, rather than traditional chemotherapy drugs that can damage healthy cells.
Liquid Biopsies
A liquid biopsy is a test that analyzes a patient’s blood to detect cancer cells or DNA fragments released by cancer cells. This non-invasive approach is less painful and less risky than traditional biopsies, which require tissue samples to be taken directly from a tumor.
Liquid biopsies are also useful for monitoring treatment response and detecting cancer recurrence. Researchers are continuing to develop new liquid biopsy technologies that can detect cancer earlier and more accurately.
Targeted Therapy
Targeted therapy is a type of cancer treatment that targets specific proteins or other molecules that help cancer cells grow and spread. This approach is different from chemotherapy, which can damage healthy cells along with cancer cells.
Targeted therapy drugs can be used alone or in combination with other cancer treatments. Researchers are continuing to develop new targeted therapy drugs and combinations to improve treatment outcomes for patients.
CAR-T Therapy
CAR-T therapy is a type of immunotherapy that involves engineering a patient’s T cells to recognize and attack cancer cells. T cells are a type of white blood cell that plays a key role in the immune system.
The CAR-T approach involves removing T cells from a patient’s blood, modifying them in a laboratory to recognize cancer cells, and then infusing them back into the patient’s body.
CAR-T therapy has shown remarkable success in treating certain types of blood cancers, including leukemia and lymphoma.
Nanotechnology
Nanotechnology is an emerging field that involves the manipulation of materials at the nanoscale level. In cancer research and treatment, nanotechnology is being used to develop new drug delivery systems that can target cancer cells more effectively.
Nanoparticles can be engineered to carry drugs directly to cancer cells, reducing side effects and improving treatment outcomes. Researchers are also exploring the use of nanotechnology for cancer imaging and diagnosis.
Artificial Intelligence
Artificial intelligence (AI) is a rapidly advancing field that is revolutionizing many aspects of healthcare, including cancer research and treatment. AI algorithms can analyze large amounts of data, including genomic and imaging data, to identify patterns and predict outcomes.
This can help researchers identify new treatment approaches and personalize treatment plans for individual patients. AI is also being used to develop new cancer detection methods, including computer-aided imaging analysis and automated pathology analysis.
Radiation Therapy
Radiation therapy is a common cancer treatment that uses high-energy radiation to kill cancer cells. Recent advances in radiation therapy technology have led to new approaches that can improve treatment outcomes while minimizing side effects.
One such approach is called stereotactic body radiation therapy (SBRT), which delivers high doses of radiation directly to the tumor while sparing nearby healthy tissue. This approach is particularly useful for treating tumors in the lungs, liver, and spine.
Liquid Biopsies for Early Detection
As mentioned earlier, liquid biopsies are a non-invasive way to detect cancer cells or DNA fragments released by cancer cells in the blood. However, researchers are also exploring the use of liquid biopsies for early cancer detection.
By analyzing circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA) in the blood, liquid biopsies can potentially detect cancer at an early stage, when it is more treatable. This approach is still in the early stages of development, but it has the potential to revolutionize cancer screening and early detection.
Precision Medicine
Precision medicine is an approach to healthcare that takes into account individual genetic, environmental, and lifestyle factors when developing treatment plans. This approach is particularly relevant in cancer treatment, where tumors can vary widely in terms of genetic mutations and other characteristics.
By analyzing a patient’s genomic and other data, healthcare professionals can develop personalized treatment plans that target the specific characteristics of their cancer. Precision medicine is already being used in some cancer treatments, and researchers are continuing to explore new applications and approaches.
Conclusion
In conclusion, recent developments in cancer research and potential breakthroughs in treatment offer new hope for patients and healthcare professionals alike. From immunotherapy and genomics to liquid biopsies and precision medicine, there are many exciting new approaches to cancer treatment that are improving outcomes and reducing side effects.
While there is still much work to be done, these developments represent a significant step forward in the fight against cancer. As healthcare professionals, it is important to stay up-to-date with the latest research and treatment approaches to ensure that our patients receive the best possible care.


























